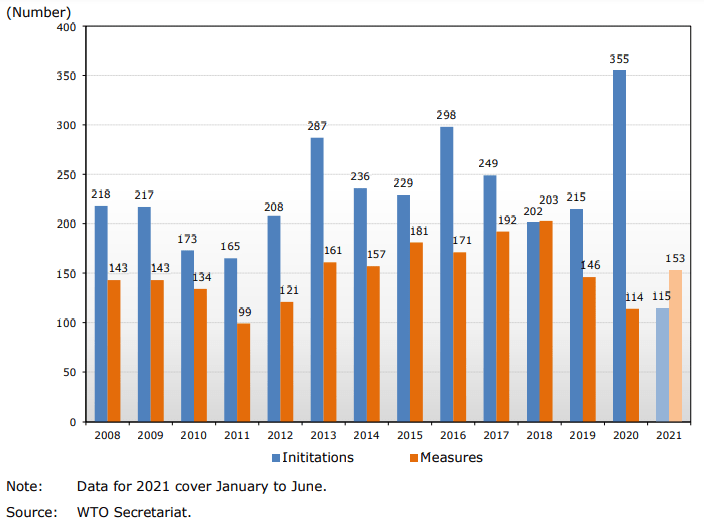
The number of anti-dumping measures initiated in the world fell in the 12 months ended in June 2021, reported the World Trade Organization (WTO).
While in that period 213 anti-dumping measures were registered, in the same period ended in June 2020 the figure reached 282 measures.
While anti-dumping investigations do not necessarily lead to the imposition of measures, an increase in the number of investigations initiated is an early indicator of a likely increase in the number of measures imposed.
During the last three periods, a total of 478 anti-dumping measures were applied.
Since the conclusion of an anti-dumping investigation can take up to 18 months, the measures applied in a given period may not necessarily be the result of investigations initiated in the same period.
Initiations of anti-dumping investigations and measures applied, 2008-21
Overall, there was little change in the products affected by the anti-dumping investigations initiated during the three periods under review. Most of the initiations focused on products in the metal sector, followed by the chemical sector and the plastics and rubber sector.
Anti-dumping measures
Regarding the countries or customs territories affected by new anti-dumping investigations, 44 exporting Members were affected during the first period, 55 during the second period and 46 in the last period.
By far, China remained the WTO Member most affected by anti-dumping initiations during the three reporting periods, accounting for 26% of all investigations.
China was followed by Vietnam and Malaysia, which accounted for 5% of all initiations.
As of October 8, 2021, only two Members had notified anti-dumping measures regarding the Covid-19 pandemic.
Brazil suspended anti-dumping duties on syringes and vacuum plastic tubes for blood collection, and Argentina suspended anti-dumping duties on syringes and parenteral solutions.
The WTO is the most important trade forum worldwide, being the only institution that deals with the rules that govern international trade between countries, through a multilateral framework of disciplines that establish the principles of liberalization, as well as the flexibilities allowed. Its main function is to ensure that trade operates as smoothly, predictably and freely as possible.
![]()

