Problems in key transportation arteries, the Panama Canal and the Red Sea, have raised the costs of transiting these maritime routes.
Since the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) first published the Trade and Development Report 2023, both negative shocks have affected maritime routes, the backbone of international merchandise trade.
By way of example, these logistical problems raised the costs of The Cato Corporation, which operated 1,178 fashion specialty stores as of February 3, 2024, in 31 states, mainly in the southeastern United States.
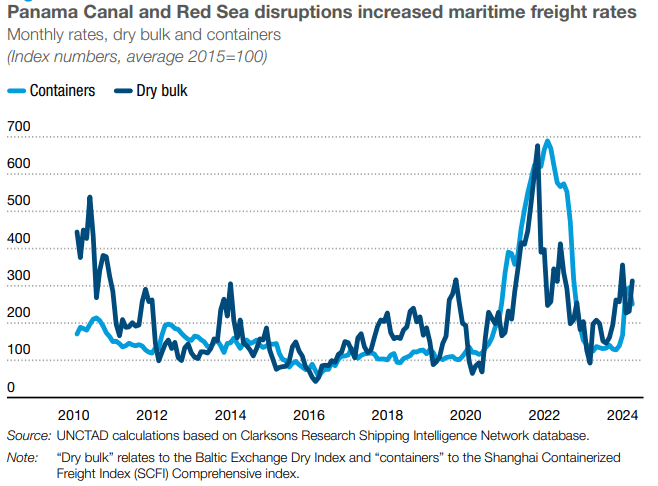
In the Panama Canal, a prolonged drought forced its operator to reduce the number of crossings, resulting in longer waiting times.
In financial terms, this increased the tolls that ships pay to pass through the canal’s various locks by as much as eight times by mid-March 2024.
According to UNCTAD, this is partly because the canal authority had increased toll rates before the onset of the water crisis, but this is also due to the fact that shipping companies have been willing to pay substantial sums in specialized auctions to secure one of the few crossing opportunities.
In addition, attacks on ships that began in the Red Sea after the Gaza war forced major shipping lines to suspend transits through Suez and divert via the Cape of Good Hope, adding 12 to 20 days of shipping.
Sea routes
A significant portion of The Cato Corporation’s goods are manufactured overseas, mainly in Southeast Asia, and pass through the Panama Canal or the Suez Canal.
Due to a sustained regional drought, the Panama Canal has reduced the number of transits by approximately 37% and has also reduced the permitted draft of vessels transiting the Panama Canal, which reduces the volume and number of containers carried by container ships and increases costs.
Recent hostilities affecting the Red Sea and Suez Canal are causing container ships to travel much longer distances around the Cape of Good Hope, increasing both the lead times for delivery of goods during key sales periods and the costs of shipping these goods.

