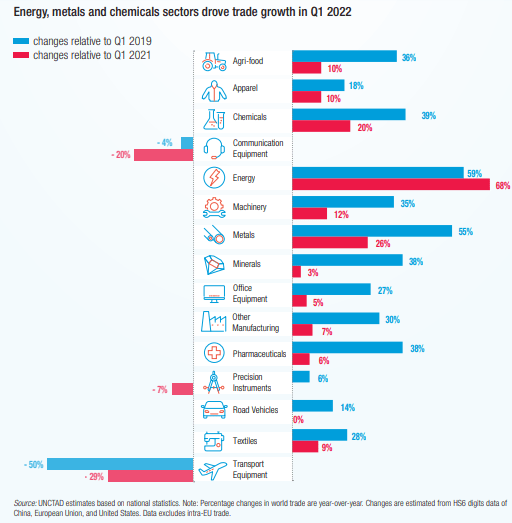
International trade in the automotive industry stagnated in growth (0%) in the first quarter of 2022, according to data from the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD).
This international trade in the first quarter of the current year increased 14% when compared to the same period in 2019, the year before the Covid-19 pandemic.
In contrast, the energy industry had the most dynamism in that same comparative, with a growth of 68% compared to the first quarter of 2020 and an increase of 59% over the same period of 2019.
Overall, UNCTAD indicated that most economic sectors recorded a significant year-on-year increase in the value of their trade in the first quarter of 2022.
High fuel prices are behind the strong increase in the value of trade in the energy sector.
Trade growth was also above average for metals and chemicals.
In contrast, trade in the transportation sector continues to be weighed down by weak aircraft orders, while trade in communications equipment also remained below its 2021 and 2019 levels.
Finally, global semiconductor shortages and logistical disruptions continue to negatively affect trade in road vehicles and precision instruments.
International trade
Toyota estimates that annual worldwide vehicle sales totaled about 83 million units in 2021.
Automotive sales are affected by a number of factors including:
- Social, political and economic conditions.
- Introduction of new vehicles and technologies.
- The costs of acquiring and operating automobiles by customers.
- Availability of parts and components Toyota needs to manufacture its products.
These factors can cause consumer demand to vary substantially from year to year in different geographic markets and across different categories of automobiles.
Global economic activity was headed for recovery in FY2022, supported by country-specific fiscal and monetary policies, as well as the gradual easing of tight restrictions due to the pandemic.
Covid-19
The automotive market faced global production constraints due to the lack of supply of parts and components caused by the impact of the pandemic, as well as tightening global supply and growing demand for semiconductors.
However, demand was sustained in countries such as the United States, China and Japan, which was a recovery from last year.
In the short term, the impact of geopolitical tensions arising from February 2022 spread around the world in the form of product price increases, making it even more difficult to forecast the future.
In the United States, there has been sustained economic activity thanks to advances in vaccination and the favorable labor and wage environment, and the government’s economic policies have contributed to a continued recovery based on strong domestic demand.
Monetary policy has now shifted toward raising interest rates to curb overheating inflation.
In Europe, although progress has been made in vaccination, there is again a growing number of Covid-19 cases, which has led to restrictions on economic activity.
In addition, Europe has been most affected by the geopolitical tensions that have arisen since February 2022, which has slowed the momentum of the recovery.
![]()

