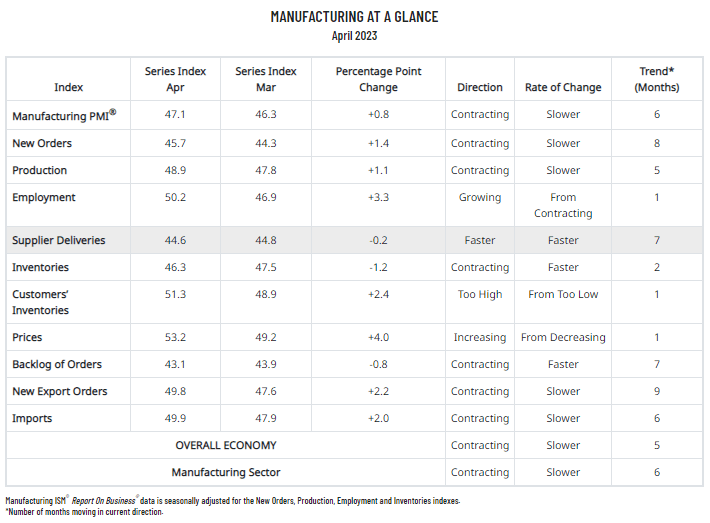
The April manufacturing index from the Institute for Supply Management (ISM), which measures the breadth of growth in the manufacturing sector, rose to 47.1 in the United States in April 2023.
In doing so, the index suggested that manufacturing activity contracted for the sixth consecutive month.
In the prior month, the ISM indicated that domestic weakness is offsetting the momentum from China‘s reopening.
The index fell from 47.7 in February 2023 to 46.3 in March, its lowest reading since May 2020.
Meanwhile, U.S. industrial production rose 0.71 percent in 2022, a worse result than in 2021, when industrial production rose 2.89 percent.
According to the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC), the recent resurgence of manufacturing activity in China poses an upside risk to the near-term outlook for the U.S. manufacturing sector, but that support could be offset by a loss of business confidence and tighter credit conditions stemming from problems in the U.S. banking sector.
ISM
In the April results, of the five sub-indices directly involved in the manufacturing PMI, only one (Employment) is in growth territory.
Of the six largest manufacturing industries, two (Petroleum & Coal Products; and Transportation Equipment) posted growth in April.
The Production index recorded a fifth month of contraction.
Three of the 10 sub-indices were above 50% in this period.
A reading above 50% indicates that the manufacturing sector is generally expanding; below 50% indicates that it is generally contracting.
The Institute for Supply Management (ISM) serves supply management professionals in more than 90 countries.
Its 50,000 members worldwide manage about $1 trillion in corporate and government supply chain purchases annually.
Founded in 1915 as the world’s first supply management institute, ISM is committed to advancing the practice of supply management to drive value and competitive advantage for its members, contributing to a prosperous and sustainable world.

