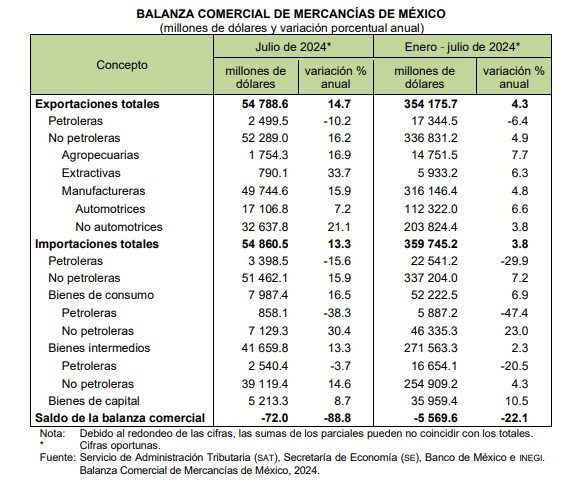
Mexico‘s manufacturing exports grew 4.8% from January to July 2024, to US$316,146.4 million.
Mexico exports to the world mainly transportation equipment, computers, electronics, food, chemicals, beverages, plastics and machinery.
Of the total sales of products from Mexico to foreign countries in the first seven months of this year, 89.3% correspond to manufactured products.
Industrial production
The global manufacturing industry is one of the largest in the world.
In 2023, Mexico remained the world’s seventh largest exporter of manufactured goods, with 463 billion dollars, an increase of 4.3% over 2022.
Mexican industry is diverse, ranging from automotive, electronics and petrochemicals to the agro-industrial and textile sectors, among others.
It also stands out for its foreign sales of advanced technology, including aerospace, biotechnology and information and flexible manufacturing and optoelectronic goods.
Mexico is also one of the world’s leading producers of automobiles.
Mexico’s manufacturing exports
Of foreign sales from January to July 2024, automotive sales were US$112,322.0 million and non-automotive sales were US$203,824.4 million, with increases of 6.6% and 3.8% in that order.
For much of the 20th century, Mexico adopted an import substitution model.
The main objective of this approach was to promote domestic production and, at the same time, reduce dependence on foreign goods.
As a result of these policies, there was a notable increase in local manufacturing in key sectors such as textiles, food and chemicals.
Subsequently, Mexico took a significant step toward trade liberalization with its entry into the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) on January 1, 1986.
This move was fundamental for the country’s integration into international trade.
In addition, on January 1, 1994, Mexico initiated the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), marking a milestone in its strategy of economic openness and regional collaboration.
New technologies
In terms of the evolution of factories globally, Xometry highlights that the industry is well positioned for further digitization.
This is due to a number of global thematic shifts that include, among others, a growing demand for production, the adoption of new manufacturing technologies, and the adjustment in value chains.

