The balance between sugar production and consumption in the world registered a surplus in the last cycle (2022-2023) and also foreseeably in the current season (2023-2024), according to data reported by the German company Südzucker AG.
Each season runs from October 1 to September 30.
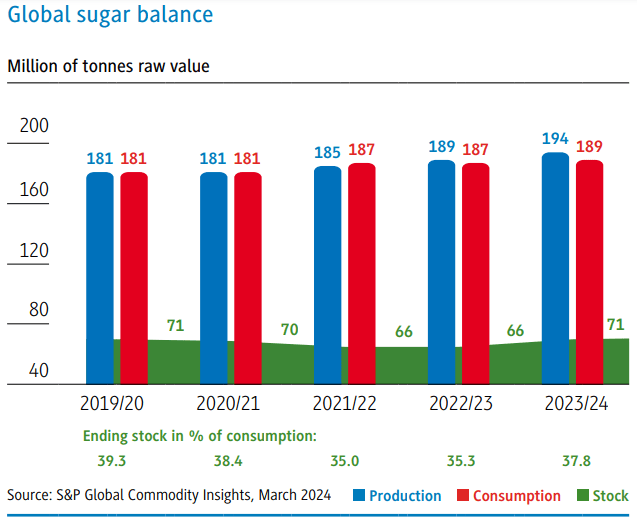
In its latest projection of the world sugar balance sheet as of March 2024, S&P Global Commodity Insights reports a surplus of 0.7 million tons for the 2022/23 sugar season.
This follows three consecutive years of deficit.
On the one hand, there was a significant increase in sugar production in Brazil and Thailand.
On the other hand, lower production was observed in Mexico, China, the European Union, India and Pakistan.
In addition, consumption remained almost stable. As a result, the ratio of inventories to consumption remained very low, at around 35%.
World sugar production and consumption
For the current 2023/24 sugar season, S&P Global Commodity Insights anticipates a surplus of 5.2 million tons of sugar.
Südzucker reports that a further increase in production is expected, especially in Brazil, Pakistan, China and Europe.
However, a decrease is expected in Thailand and Mexico.
In addition, higher consumption is expected. Thus, the ratio of inventories to consumption is expected to remain low, just below 38%.
Trend
Throughout history, the international sugar market has gone through phases of limited supply, which has led to an increase in sugar prices and industry profit margins.
This, in turn, has caused an expansion in the industry, resulting in oversupply and a consequent fall in sugar prices and profit margins.
In addition, according to the Brazilian company Cosan Limited, ethanol and sugar prices can vary for various reasons such as:
- Decrease in the demand for vehicles with internal combustion engines.
- Variations in gasoline prices.
- Changes in competitors’ production capacities.
- Availability of substitute goods for ethanol and sugar.

