The U.S. automotive industry can be divided into three distinct regions: the Midwest region, the Southeast region, and the rest of the United States.
In 2022, U.S. automotive production accounted for 66.5% of production in North America and 11.4% globally.
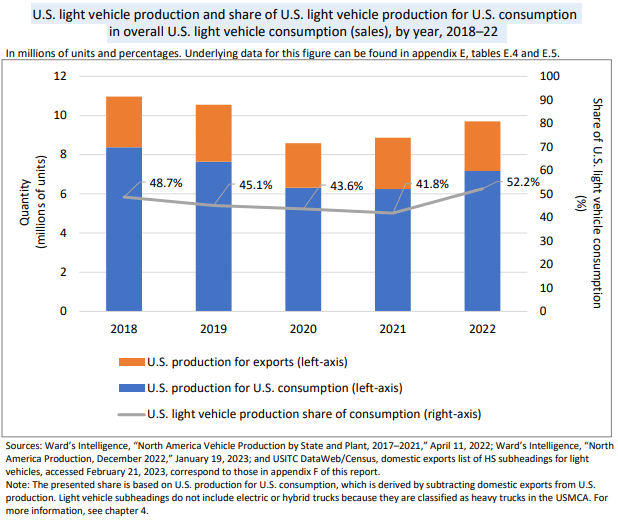
Also, according to the U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC), the industry employed more than 250,000 people in vehicle manufacturing, more than half a million people in parts production, as well as sales and repair, and more than 162,000 people in motor vehicle body and trailer manufacturing in 2021.
For the Midwest and Southeast regions, the decline between 2018 and 2022 is mostly accounted for in 2020; however, production has been slowly increasing since then.
On the other hand, production in the rest of the U.S. increased 39% from 2018 to 2022 largely due to increased demand for electric vehicles.
The onset of the Covid-19 pandemic saw plant closures in the U.S., with more than 40% of the automotive workforce suspended or laid off in March and April 2020.
In addition, even after plants reopened, the U.S. auto industry grappled with several supply chain issues.
Automotive Industry
The global semiconductor shortage led automakers to shut down production for a second time or reduce the number of shifts or vehicle production per shift.
Regionally, the North American automotive industry is comprised of vehicle and vehicle parts production in the United States, Mexico and Canada.
All three countries are among the world’s leading vehicle producers, with significant production of a wide range of vehicles.
In recent years, the North American region has been negatively affected by a number of factors, including plant closures associated with the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic, supply chain constraints such as the global semiconductor shortage, and a shortage of skilled labor.
These interrelated factors (as well as others) resulted in production declines in all three countries over the past several years, with most of these declines occurring in 2020.

