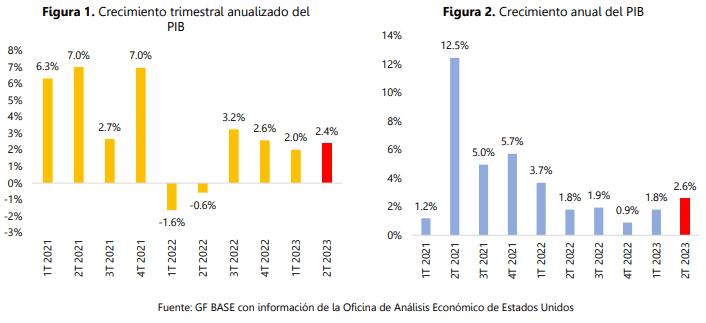
Banco Base published an analysis on the United States economic projection, after announcing that the U.S. GDP grew during the second quarter of 2023 at an annualized quarterly rate of 2.4% and at an annual rate of 2.6 percent.
Therefore, GDP growth for the first half of the year is 2.18% annualized (compared to the same period in 2022) and shows an expansion of 6.18% from pre-pandemic levels.
During the second quarter, the U.S. economy grew 2.4% quarter-over-quarter annualized, showing an acceleration from the first quarter of the year.
Consumption was the largest contributor to second quarter GDP growth in the United States.
Internally, it highlights that consumers are prioritizing their spending on services, trying to make up for what they lost in the pandemic.
But the banking problem continues: the Federal Reserve used 105.56 billion dollars in emergency loans to banks as of July 19, 97.51% explained by the term liquidity program and, as a second aspect, credit granting decreased by 51.69 billion dollars or 0.43% between March 15 and July 12.
Economic projection
Banco Base indicated that the probability of recession for the next 12 months reached a year high of 94.7% in May, before declining to 78.8% in July.
The Fed staff no longer expects a recession this year.
At the same time, the debt ceiling was removed until 2025. As of July 20, U.S. debt reached $32.592 trillion. This represents an increase of $1.128 trillion, or 3.58%, compared to the end of May.
Meanwhile, the fiscal deficit grew significantly in the first nine months of the fiscal year. It increased by 170.4%, marking the highest growth since 2020. That year, the deficit rose by 267.3% due to pandemic-related support measures.
By June, the fiscal deficit reached $1.393 trillion, equivalent to 8.49% of U.S. GDP.
Lastly, inflation has shown a positive trend. It has decelerated for 12 consecutive months and is projected to end the year at 3% annually.

