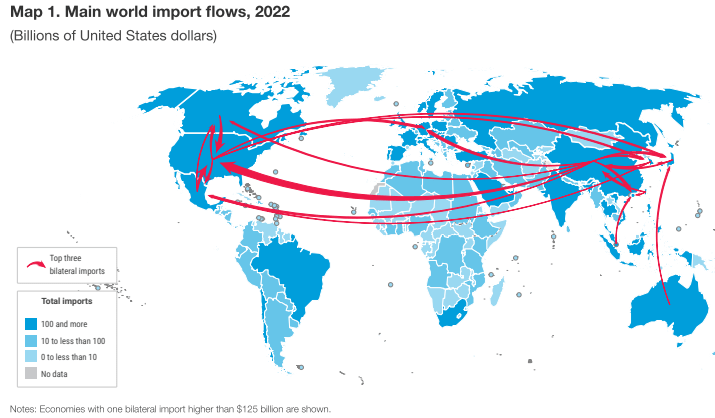
The world’s main bilateral merchandise trade flows are between China and the United States, and between their respective neighboring economies, according to UNCTAD data.
In 2022, the United States imported $576 billion worth of goods from China and China imported $179 billion worth of goods from the United States.
China’s trade (exports and imports) with Hong Kong (China), Japan, Taiwan Province of China, and the Republic of Korea amounted to $1.47 trillion.

U.S. trade with Mexico and Canada was worth US$1.59 trillion.
Intraregional trade was most pronounced in Europe and Asia.
In 2022, 68% of all European exports went to trading partners in the same continent.
In Asia, this rate was 59 percent, and in Oceania, Latin America and the Caribbean, Africa and North America, the main trading partners were extra-regional.
Merchandise trade
In 2022, merchandise exports and imports increased significantly, by more than 10 percent in developed economies and 12 percent in developing economies in Asia and Oceania.
African and American developing economies experienced the largest increase in exports (16.9 percent).
African and American developing economies experienced the largest increase in exports (16.9 percent).
In terms of imports, developing economies in the Americas recorded the largest increase (21.4 percent), and African developing economies ranked second (18.9 percent).
In developing Asia and Oceania, imports increased much less (10.2 percent).
The value of world merchandise exports increased 11.4 percent in 2022.
It was the second year of solid growth after two consecutive years of decline during the COVID-19 pandemic.
World exports totaled $24.9 billion, $2.5 billion higher than the previous year.
However, in the first half of 2023, the value of exports declined 4.6% year over year.
In 2022, almost all developed economies recorded an increase in exports, with the exception of Belarus (-42.7 percent) and Ukraine (-34.8 percent).